Netty由JBOSS提供的Java开源框架,是一个异步的、基于事件驱动的网络应用框架。本质是一个NIO框架。
层次关系:netty--->NIO--->原生JDK I/O和网络—-->TCP/IP。
在高并发应用场景中,同步NIO是性能很低的,也是基本不可用的,一般 Web 服务器都不使用这种 IO 模型。在 Java 的实际开发中,不会涉及这种 IO 模型,但是此模型还是有价值的,其作用在于其他 IO 模型中可以使用NIO模型作为基础,以实现其高性能。
1.IO多路复用
采用 IO 多路复用模型可以避免同步NIO 模型中轮询等待的问题。
IO多路复用是指内核一旦发现进程指定的一个或者多个IO条件准备读取,它就通知该进程。
在处理IO的时候,阻塞和非阻塞都是同步IO。只有使用了特殊的API才是异步IO。如下图所示:
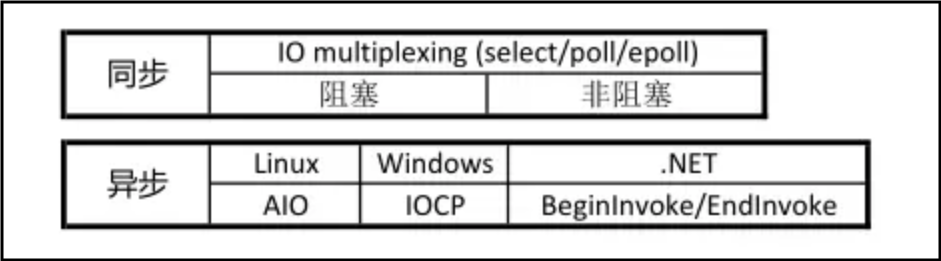
目前支持 IO 多路复用的系统调用有 select、epoll 等。几乎所有的操作系统都支持select系统调用,它具有良好的跨平台特性。epoll 是在 Linux 2.6 内核中提出的,是 select 系统调用的 Linux 增强版本。
在 IO 多路复用模型中通过 select/epoll 系统调用,单个应用程序的线程可以不断地轮询成百上千的 socket 连接的就绪状态,当某个或者某些 socket 网络连接有 IO 就绪状态时就返回这些就绪的状态(或者说就绪事件)。
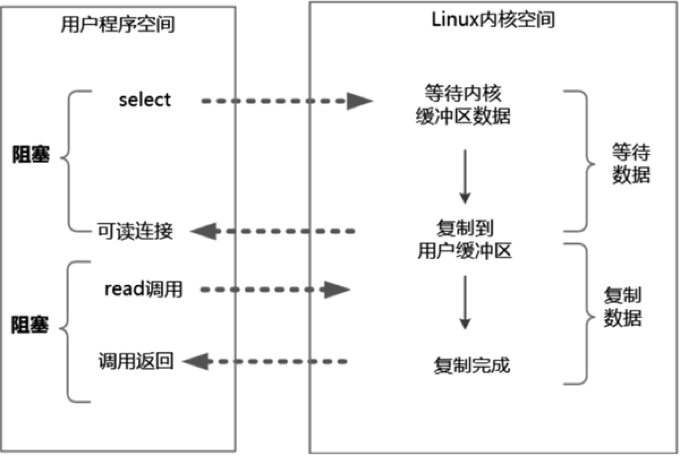
IO 多路复用模型的 read 系统调用流程如上图所示。
举个例子来说明 IO 多路复用模型的流程。发起一个多路复用 IO 的 read 操作的系统调用,具体流程如下:
(1)选择器注册。首先,将需要 read 操作的目标文件描述符(socket连接)提前注册到 Linux 的 select/epoll 选择器中,在 Java 中所对应的选择器类是 Selector 类。然后,开启整个 IO 多路复用模型的轮询流程。
(2)就绪状态的轮询。通过选择器的查询方法,查询所有提前注册过的目标文件描述符(socket连接)的 IO 就绪状态。通过查询的系统调用,内核会返回一个就绪的 socket 列表。当任何一个注册过的 socket 中的数据准备好或者就绪了就说明内核缓冲区有数据了,内核将该 socket 加入就绪的列表中,并且返回就绪事件。
(3)用户线程获得了就绪状态的列表后,根据其中的 socket 连接发起 read 系统调用,用户线程阻塞。内核开始复制数据,将数据从内核缓冲区复制到用户缓冲区。
(4)复制完成后,内核返回结果,用户线程才会解除阻塞的状态,用户线程读取到了数据,继续执行。
1.1.IO多路复用的特点
IO 多路复用模型典型的特点是:IO 多路复用模型的 IO 涉及两种系统调用,一种是 IO 操作的系统调用,另一种是 select/epoll 就绪查询系统调用。IO 多路复用模型建立在操作系统的基础设施之上,即操作系统的内核必须能够提供多路分离的系统调用 select/epoll。
IO 多路复用模型的优点是一个选择器查询线程可以同时处理成千上万的网络连接,所以用户程序不必创建大量的线程,也不必维护这些线程,从而大大减少了系统的开销。与一个线程维护一个连接的阻塞 IO 模式相比,这一点是 IO 多路复用模型的最大优势。
通过 JDK 的源码可以看出,Java 语言的 NIO 组件在 Linux 系统上是使用 epoll 系统调用实现的。所以,Java 语言的 NIO 组件所使用的就是 IO 多路复用模型。
IO 多路复用模型的缺点是,本质上 select/epoll 系统调用是阻塞式的,属于同步 IO,需要在读写事件就绪后由系统调用本身负责读写,也就是说这个读写过程是阻塞的。要彻底地解除线程的阻塞,就必须使用异步 IO 模型。
1.2.IO多路复用与NIO
和 NIO 模型相似,多路复用 IO 也需要轮询。负责 select/epoll 状态查询调用的线程,需要不断地进行 select/epoll 轮询,以找出达到 IO 操作就绪的 socket 连接。
IO 多路复用模型与NIO 模型是有密切关系的,具体来说,注册在选择器上的每一个可以查询的 socket 连接一般都设置成同步非阻塞模型,只是这一点对于用户程序而言是无感知的。
2.Netty简单demo
下面以Netty搭建一个构建Http RPC框架为例。
2.1.Server端demo
包含NettyHttpServer、HttpServerHandler和MediaInt。
NettyHttpServer代码如下所示:
public class NettyHttpServer implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>,Ordered{
public void start() {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
EventLoopGroup childGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup parentGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//accept,read,write
serverBootstrap.group(parentGroup, childGroup);
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // (3)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { // (4)
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//http解码,编码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(1048576));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerHandler());
}
})
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // (5)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); //
ChannelFuture future = null;
try {
future = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
public int getOrder() {
return 20;
}
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent arg0) {
start();
}
}HttpServerHandler代码如下所示:
public class HttpServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
Object result = new Object();
try {
if(msg instanceof FullHttpRequest){
String content = ((FullHttpRequest)msg).content().toString(Charset.defaultCharset());
System.out.println(content);
//首先根据request content获取是哪个controller,并且要获取对应的请求方法
RequestParam requestParam = JSONObject.parseObject(content, RequestParam.class);
String command = requestParam.getCommand();
//然后去执行相对应的 方法
BeanMethod beanMethod = Media.commandBeans.get(command);
if(beanMethod !=null){
Object bean = beanMethod.getBean();
Method m = beanMethod.getM();
Class<?> paramType = m.getParameterTypes()[0];
Object param=null;
if(paramType.isAssignableFrom(List.class)){
param = JSONArray.parseArray(JSONArray.toJSONString(requestParam.getContent()), paramType);
}else{
param = JSON.parseObject(JSONObject.toJSONString(requestParam.getContent()), paramType);
}
result = m.invoke(bean, param);
ResponseParam responseParam = new ResponseParam();
responseParam.setCode("00000");
responseParam.setResult(result);
result = responseParam;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
ResponseParam responseParam = new ResponseParam();
String failMsg = "您的请求异常!";
responseParam.setCode("33333");
responseParam.setResult(failMsg);
result = responseParam;
}
DefaultFullHttpResponse response =new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus .OK, Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(JSONObject.toJSONString(result).getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset()))); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION,HttpHeaderValues.KEEP_ALIVE); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH,response.content().readableBytes()); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE,"text/plain");
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(response);
}
}MediaInt代码如下所示:
public class MediaInit implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>,Ordered{
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
//根据Spring容器,找到包含有Controller注解的所有bean
Map<String,Object> beans = event.getApplicationContext().getBeansWithAnnotation(Controller.class);
Map<String,BeanMethod> commandBeans = Media.commandBeans;
for(String key : beans.keySet()){
Object bean = beans.get(key);
Method[] ms = bean.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m : ms){
if(m.isAnnotationPresent(Remote.class)){
Remote remote = m.getAnnotation(Remote.class);
String command = remote.value();
BeanMethod beanMethod = new BeanMethod();
beanMethod.setBean(bean);
beanMethod.setM(m);
commandBeans.put(command, beanMethod);
}
}
}
}
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}2.2.Client端demo
包含NettyHttpClient和HttpClientHandler。
NettyHttpClient代码如下所示:
public class NettyHttpClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
b.group(workerGroup); // (2)
b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); // (3)
b.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // (4)
b.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(1048576));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientHandler());
}
});
// Start the client.
ChannelFuture f = b.connect("localhost", 8080).sync(); // (5)
String uri ="http://localhost:8080/";
RequestParam requestParam = new RequestParam();
requestParam.setCommand("productPlanSearch");
requestParam.setContent("1");
String requestContent = JSONObject.toJSONString(requestParam);
ByteBuf content = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(requestContent.getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset()));
DefaultFullHttpRequest request = new DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1,
HttpMethod.POST, uri , content );
request.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION,HttpHeaderValues.KEEP_ALIVE);
request.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH,request.content().readableBytes());
request.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE,"text/plain");
f.channel().writeAndFlush(request);
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
ResponseParam response = (ResponseParam)f.channel().attr(AttributeKey.valueOf("httpResultKey")).get();
if(response.getCode().equals("00000")){
System.out.println(response.getResult());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}HttpClientHandler代码如下所示:
public class HttpClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if(msg instanceof DefaultHttpResponse){
}
if(msg instanceof FullHttpResponse){
String result = ((FullHttpResponse)msg).content().toString(Charset.defaultCharset());
ResponseParam response = JSONObject.parseObject(result,ResponseParam.class);
ctx.channel().attr(AttributeKey.valueOf("httpResultKey")).set(response);
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
}dubbo底层网络通信也用得是netty,dubbo协议默认是长连接,客户端一次连接会发送多个数据包,当客户端闲置的时候通过心跳检测来维持长连接通信。